![{{ $node["Process LLM Response"].json.wp_title }}](https://nuralwire.online/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/bitnews_-now.formatX-1-32.jpg)
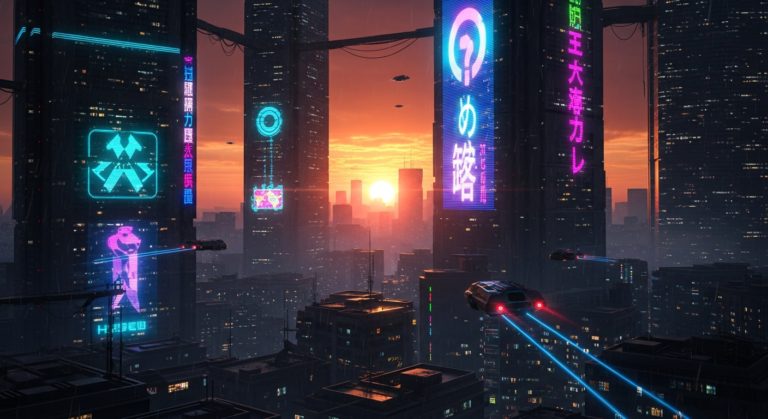
GLOBAL — A widespread power outage in San Francisco on Saturday caused significant disruptions, including the immobilization of Waymo’s autonomous vehicles. The incident exposed a critical vulnerability in the current generation of self-driving technology: reliance on functioning infrastructure.
What Happened
A major power outage struck San Francisco, affecting approximately 130,000 Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) customers. The outage, the cause of which is still under investigation, had an unexpected consequence: Waymo’s autonomous vehicles became stranded on city streets. Social media was flooded with images and videos of stationary Waymo SUVs, contributing to traffic congestion. The vehicles appeared unable to navigate intersections where traffic lights were not functioning.
This incident contrasts with claims made by Tesla CEO Elon Musk, who tweeted that Tesla’s “Robotaxis were unaffected by the SF power outage,” implying that Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) system was able to navigate the same streets without issue. While difficult to verify independently, the social media posts showing stationary Waymo vehicles paint a clear picture of the challenges faced by autonomous driving systems in unexpected circumstances.
Why It Matters Now
The San Francisco power outage serves as a stark reminder that autonomous vehicles are not yet fully independent. While significant progress has been made in self-driving technology, these systems still rely on a complex ecosystem of sensors, software, and infrastructure. The Waymo incident underscores the importance of redundancy and fallback mechanisms in autonomous driving systems.
The incident also reignites the debate about the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles in real-world scenarios. While proponents tout the potential for increased safety and efficiency, critics point to the limitations and vulnerabilities of these systems, particularly in unpredictable or edge-case situations. This event provides concrete evidence for those concerns.
How It Works (Plain English)
Waymo’s autonomous vehicles, like many self-driving systems, use a combination of sensors, including cameras, lidar, and radar, to perceive their surroundings. These sensors feed data into sophisticated software algorithms that interpret the environment, plan a route, and control the vehicle’s steering, acceleration, and braking. A crucial element of this perception is the ability to detect and respond to traffic signals.
In the event of a power outage, traffic lights cease to function, requiring drivers to rely on established right-of-way rules and visual cues. The Waymo vehicles appear to have been unable to effectively process the absence of functioning traffic lights, leading them to stop and remain stationary. This suggests that the system’s reliance on automated traffic signal detection is a critical dependency.
Real-World Impact
The immediate impact of the Waymo vehicle strandings was increased traffic congestion in affected areas of San Francisco. This caused delays for commuters and businesses, highlighting the potential for autonomous vehicle malfunctions to disrupt daily life. More broadly, the incident could impact public trust in autonomous driving technology.
The incident also provides valuable data for Waymo and other autonomous vehicle developers. By analyzing the performance of their systems during the power outage, they can identify areas for improvement and develop more robust fallback mechanisms. This could lead to updates in sensor fusion algorithms, enhanced decision-making logic, or the integration of alternative navigation strategies.
Limitations & Risks
The primary limitation exposed by the San Francisco power outage is the reliance of current autonomous driving systems on functioning infrastructure. This dependency creates a vulnerability to power outages, natural disasters, and other unforeseen events. The incident also highlights the challenges of designing autonomous systems that can effectively handle edge cases and unexpected situations.
Other limitations and risks associated with autonomous vehicles include:
- Safety: While autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce accidents caused by human error, they also pose new safety risks related to software malfunctions, sensor failures, and unpredictable environmental conditions.
- Reliability: The reliability of autonomous systems can be affected by weather conditions, road markings, and other factors.
- Privacy: Autonomous vehicles collect vast amounts of data about their surroundings and occupants, raising privacy concerns about how this data is used and protected.
- Cost: The cost of developing, deploying, and maintaining autonomous vehicles is currently high, which could limit their accessibility to certain segments of the population.
Competitive Landscape
\